9. Simulate a subsurface mooring with a Cable
The identification tag for this tutorial is PDS-AAK. Input files for this tutorial are in the folder named PDS-AAK in tutorial input files.
9.1. Tutorial overview
This tutorial covers:
- Creating a simple Subsurface mooring using an ExtMass and an ExtMassCylinder
- Anchoring a cable to the seabed
9.2. Setting up the Cable
- Create a new project in PST.
- Save the project to a new folder.
- In the environment input file, set
$WaterDepth 50. - Create a new Cable DObject with the default name Cable_1.
- Click the State button on the top project ribbon to define the state of Cable_1.
- Place Node0 at (0,0,25).
- Place NodeN at (0,0,50).
- Set the number of elements to 10.
- Set the length of cable to 25 m. Click Generate.
- Pin NodeN to the seabed by setting
$NodeNStatic 1in the cable input file. - Create a DCableSegment feature in the library called wire_rope_2in.
- Change the properties to the values shown below. The properties listed represent generic 2 inch wire rope.
// Axial Rigidity
$AxialRigidityMode 0
$EA 2e8
// Fluid loading
$CDc 1.5
$CDt 0.01
$CAc 1
// Mechanical
$EI1 1e3
$EI2 1e3
$GJ 1e3
$Diameter 0.05
$Density 5000
$AxialDampingMode 1
$AxialReferenceDampingRatio 0.5
$BCID 0
$TCID 0
$CE 1
// Strain Limit
$ElongationLimitMode 0
- Reference the wire rope feature in the cable input file by adding
$CableSegment wire_rope_2in 20.
9.3. Add a mid-line acoustic release
To add an acoustic release to the mooring line, an ExtMassCylinder will be used.
- Add the following line to the cable input file:
$ExtMassCylinder AcousticRelease 10 - With the cursor on the ExtMassCylinder line in the input file, press F12. A prompt appears to create an extMassCylinder feature called AcousticRelease in the Library. Select Create.
- Set
$ExtMassType 1.
By setting $ExtMassType 1, there are now some additional follower properties that need to be defined.
- Right click on
$ExtMassType 1and select Resolve follower properties.
This property flag defines how the weight of the ExtMass or ExtMassCylinder is calculated. In this case, the weight will be calculated with the $Mass and $WeightInWater properties instead of $Density.
- Set the mass of the ExtMassCylinder to 36 kg with
$Mass 36. - Set the weight in water to 28 kg with
$WeightInWater 28. - Set the diameter of the cylinder to be 0.13 m.
- Set the length of the cylinder to be 0.946 m.
- Set the normal drag coefficient to 0.78 (
$CD 0.78) and the axial drag coefficient to 0.85 ($CDAxial 0.93).
9.4. Add a buoy
To represent a spherical float at the end of Cable_1, an ExtMass will be used.
- Add the following line to the Cable_1 input file:
$ExtMass buoy 0 - With the cursor on the ExtMass line in the input file, press F12. A prompt appears to create an ExtMass feature called float in the feature library. Select Create.
The default density of the ExtMass is 1025 kg/m3. This is approximately the density of seawater, so the buoy would be neutrally buoyant. A buoyant float can be represented by using an ExtMass with a density lower than the surrounding fluid. This is common practice to model a surface buoy or mid-line floats.
- Change the density to 300 kg/m3 to create a positively buoyant float.
- Set the diameter of the weight to 1 m.
- Look at the mooring in the Visualizer by pressing F4.
9.5. Run the simulation
- Specify a 2.0 m/s uniform current with a heading of 90 degrees.
- Set the length of simulation to 60 seconds and run the simulation.
- View the results in PostPDS.
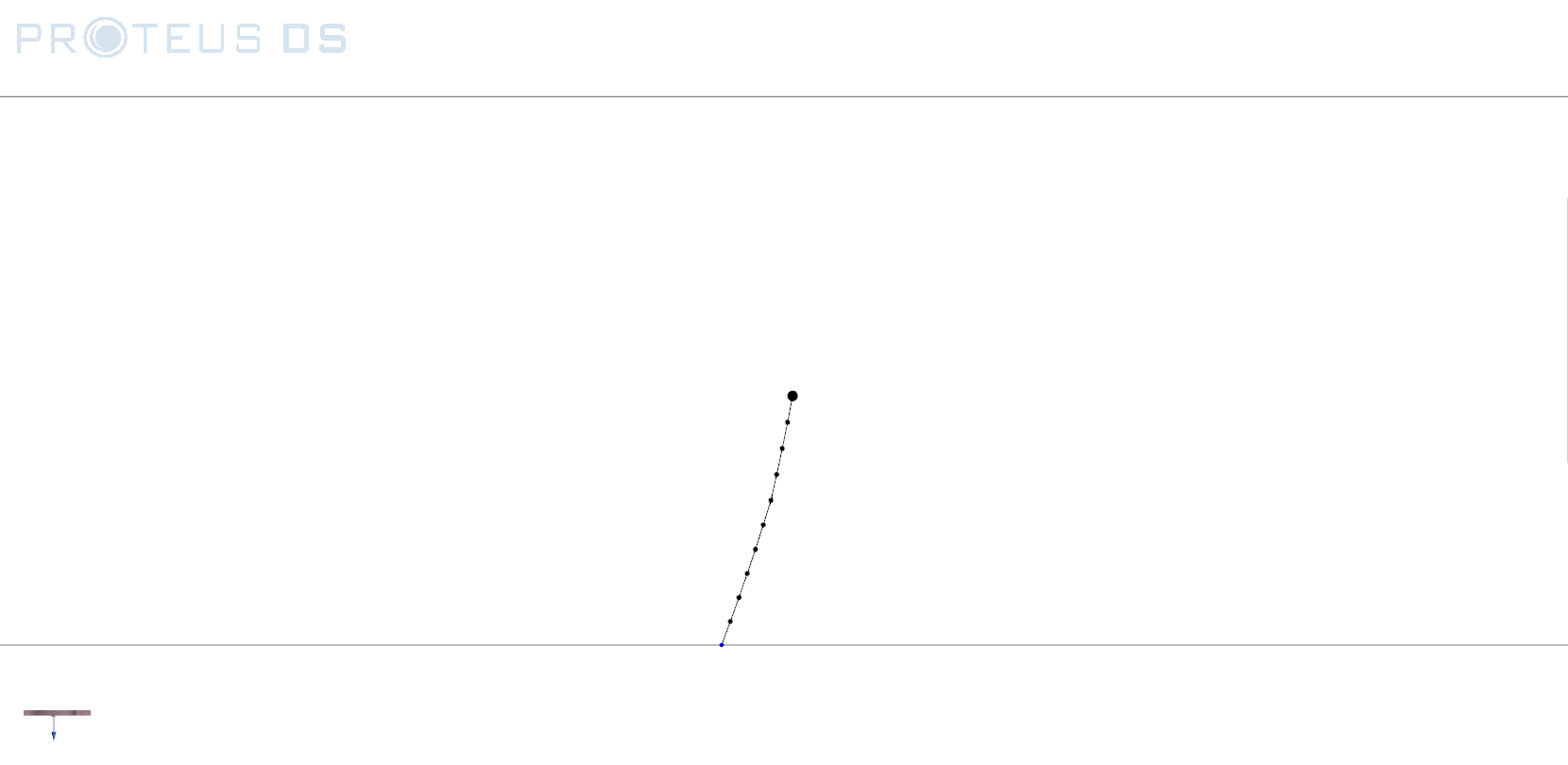

Fig. 9.1 Subsurface mooring visualized in PostPDS using report mode.
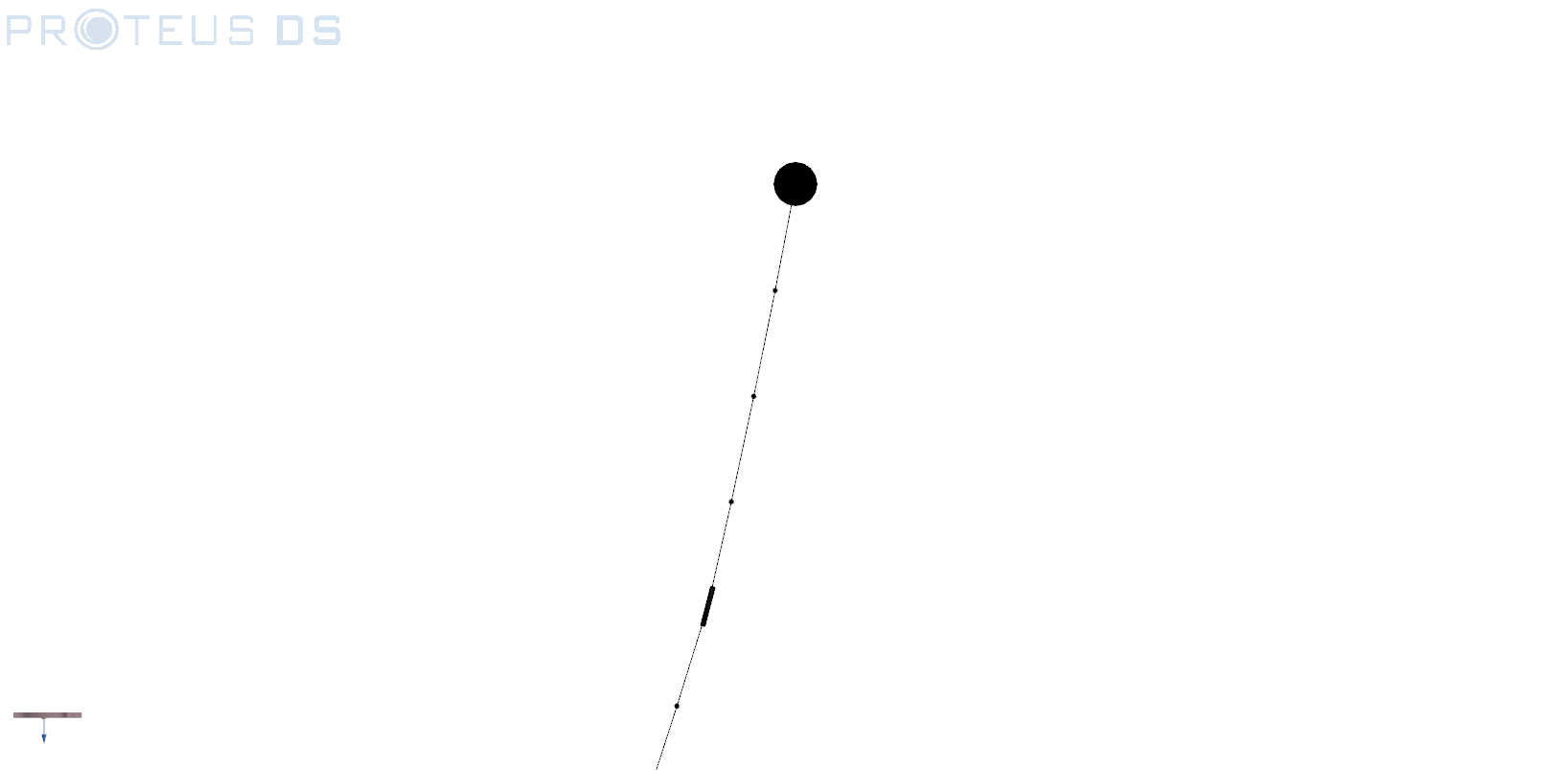
Fig. 9.2 Acoustic release and buoy visualized in PostPDS using report mode.